What is a heater pump?
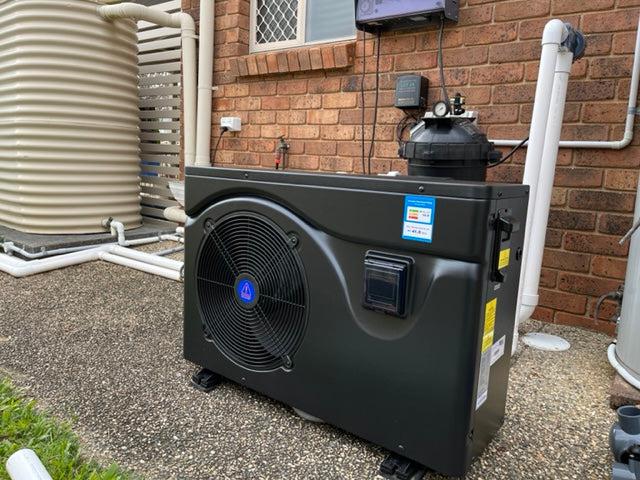

A pool heat pump, often referred to as a heat pump pool heater, is a device specifically designed to heat the water in a swimming pool. It operates by extracting heat from the surrounding air and transferring it to the pool water. This method of heating is energy-efficient and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for pool owners looking to maintain comfortable water temperatures in outdoor pools. Essentially, a pool heat pump is a heating system that uses the warmth present in the air to warm the pool water, extending the swimming season and ensuring a pleasant pool experience.
The basic components of a heat pump system:
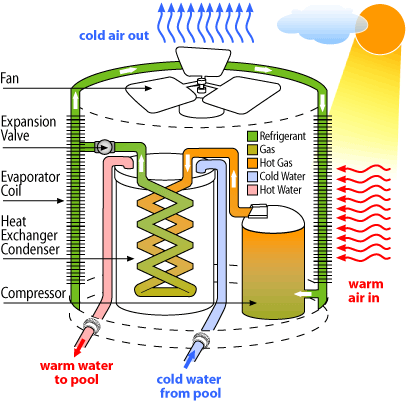
A pool heat pump system comprises several essential components to efficiently warm pool water. The basic components of a pool heat pump system include:
1. Evaporator Coil: This component is responsible for absorbing heat from the surrounding air. It’s typically located at the air intake side of the heat pump.
2. Compressor: The compressor plays a critical role in the heat pump’s operation. It pressurizes the low-temperature, low-pressure gas from the evaporator and compresses it into a high-temperature, high-pressure gas.
3. Condenser Coil: The condenser coil is where the hot, pressurized gas releases its heat to the pool water. It’s located on the water discharge side of the heat pump.
4. Refrigerant: The refrigerant is the heat transfer medium within the system. It cycles between the evaporator and condenser coils, changing from a liquid to a gas and back again as it absorbs and releases heat.
5. Fan: A fan is used to draw in outside air and direct it over the evaporator coil. This airflow helps in heat exchange with the refrigerant.
6. Expansion Valve: The expansion valve reduces the pressure of the refrigerant, causing it to cool and return to a liquid state as it re-enters the evaporator coil, ready to absorb more heat.
7. Cabinet or Housing: The cabinet or housing encases and protects the internal components of the heat pump system, keeping them safe from the elements.
8. Control Panel: Most modern pool heat pumps come with digital control panels. These panels allow you to set and monitor the desired pool temperature and operating parameters.
These components work in tandem to extract heat from the surrounding air, intensify that heat, and then transfer it to the pool water. This process provides an efficient means of maintaining comfortable water temperatures in the pool, extending the swimming season, and ensuring an enjoyable and cost-effective pool experience.
The process of a heater pump
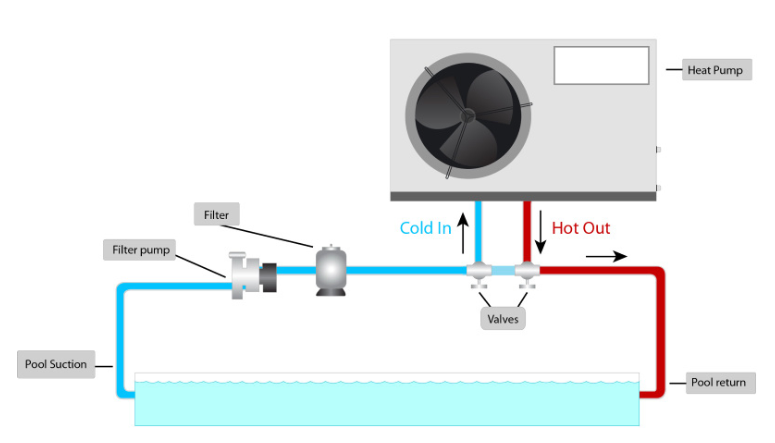
When it comes to the mechanics of a pool heat pump, it’s a straightforward yet efficient process. As the pool water circulates through the pump, it first encounters a filter and then the heat pump heater. This innovative heater comprises a fan that pulls in outside air, guiding it over the evaporator coil. Inside this coil, liquid refrigerant undergoes a transformation, absorbing heat from the ambient air and evolving into a gas. The now-warm gas advances through the compressor, where its temperature further elevates, forming a hot gas.
This scorching gas is then directed through the condenser, responsible for transferring the accumulated heat to the pool water coursing through the heater. The heated water, now revitalized, returns to the pool to maintain an enjoyable swimming experience. The gas, having released its heat within the condenser coil, undergoes a transformation back into a liquid state, initiating the entire cycle once more.
For enhanced efficiency, advanced heat pump pool heaters typically employ scroll compressors, distinguishing them from standard units with reciprocal compressors. These systems operate optimally when exposed to outdoor temperatures exceeding 45ºF–50ºF. The colder the external air they draw from, the less efficient they become, potentially resulting in higher energy costs. Nevertheless, since most pool use occurs during warmer and milder weather, this limitation is rarely a concern for pool owners.
How to choose a pool heater pump?

Choosing the right pool heat pump is essential to ensure that your pool stays comfortably warm and that you get the best value for your investment. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a pool heat pump:
1. Pool Size: Determine the size of your pool in gallons or cubic feet. This information will help you calculate the heating capacity required for your pool. A heat pump’s output is typically measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units) or kilowatts, and you’ll want a pump that can handle the volume of water in your pool.
2. Climate: Consider the climate in your area. Pool heat pumps work more efficiently in warm and mild climates. In colder regions, the effectiveness of a heat pump may be reduced, so you might need a larger unit or consider alternative heating options.
3. Energy Efficiency: Look for a heat pump with a high coefficient of performance (COP). A higher COP indicates better energy efficiency. This means the pump will produce more heat for every unit of electricity consumed.
4. Installation and Sizing: Consult with a professional to determine the right size and installation requirements for your specific pool. Proper sizing and installation are crucial for optimal performance and energy efficiency.
5. Brand and Quality: Choose a reputable brand known for producing reliable and durable pool heat pumps. Read reviews and seek recommendations from pool professionals or other pool owners.
6. Features: Consider additional features such as digital controls, timers, and automation options. Some heat pumps offer smart integration, allowing you to control the unit remotely via a smartphone app.
7. Warranty: Check the warranty offered by the manufacturer. A longer warranty period can provide peace of mind and may indicate the manufacturer’s confidence in their product.
8. Noise Level: Heat pumps can produce some noise, so consider the noise level of the unit, especially if your pool area is close to neighbors or outdoor living spaces.
9. Cost: Compare the initial purchase price, installation costs, and expected operating expenses. While heat pumps are energy-efficient, they may have a higher upfront cost compared to other heating options.
10. Maintenance: Inquire about maintenance requirements and costs. Regular maintenance can help prolong the life of your heat pump and keep it operating efficiently.
11. Environmental Impact: If you’re environmentally conscious, consider the environmental impact of your choice. Heat pumps are generally considered eco-friendly as they transfer heat rather than generate it.
12. Consult a Professional: For the best results, it’s advisable to consult with a pool professional or HVAC expert who can assess your specific needs and recommend the most suitable heat pump for your pool.
By carefully considering these factors and seeking expert advice, you can choose a pool heat pump that meets your pool heating needs, energy efficiency goals, and budget.